Risk management is part of strategic management
Every entrepreneur and every company somehow knows and manages its risks. The only question is in what way: unconsciously in the background or in some systematic way. Knowing the risks and the ability to avoid them are among the basic elements of the managerial self-preservation instinct.
Risks are potential problems that may or may not occur. They are situations that can put an organization at risk and risk management therefore helps to prevent, mitigate or prepare for these situations. If you have a plan for what you will do about them, you will be better prepared for them. So risk management in a practical sense should be a natural part of planning and managing a company, it's not some disconnected set of spreadsheets.
- You can never estimate all the risks, no matter how hard you try
- Some risks you can influence, others may occur without your influence
- Risks change over time
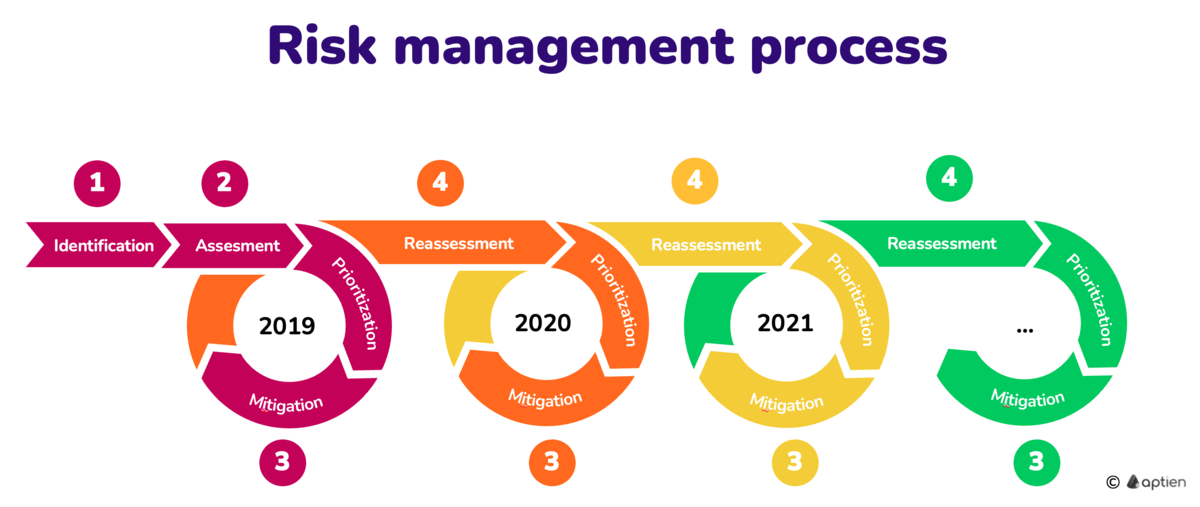
Risk management is a continuous process, just like managing a business. The whole process is continuously y going round and round, so that all current risks are properly treated and reassessed over time. Risks must be continuously monitored, reassessed and treated. Like other plans, they are set once in a while and constantly adjusted according to the situation. Risk management works in a similar way. Reassessment typically has an annual cycle.
Risk management can be implemented throughout the organization or just in a selected area
An organization typically implements risk management in the area where it is necessary especially for its main processes. Information security and cybersecurity risks are also a very common area where the company starts with risk management. The scope, i.e. the scope of risk management, must be established before starting the risk analysis. Most often:
- Company-wide risk management
- Workplace safety risks (OHS)
- Financial risks
- Information security risks
- Cyber security risks
- And more
Risk management process in the organisation
Risk management in companies and organizations focuses on the identification, analysis and subsequent mitigation of risks. Risk management is a continuing process based on the principle of continuous improvement. There are four basic phases of risk management:
- Risk identification - identifying and searching for risks related to the organization's activities
- Risk assessment - primarily assessing the impact of risks and estimating the probability of occurrence for each risk
- Risk prioritization - decide of priorities, on which risks to focus on
- Mitigation and countermeasures - decide mitigation strategy and taking effective and controllable countermeasures and actions (CAPA)
- Reassessment - revision and monitoring of the state of risks - reassessment of the results of measures and reassessment of risks
In order to deal with all of these risk management activities and processes, you need to have a place where you can store and share this information. You can conveniently perform all of these risk management steps in Aptien. It allows you to
- Develop a risk catalog (list) where you describe each individual risk using a risk card with impacts, likelihood and other context
- Create a risk matrix that allows you to prioritize risks
- Create measures, corrective and preventive actions and manage work on them, which will allow continuous assessment
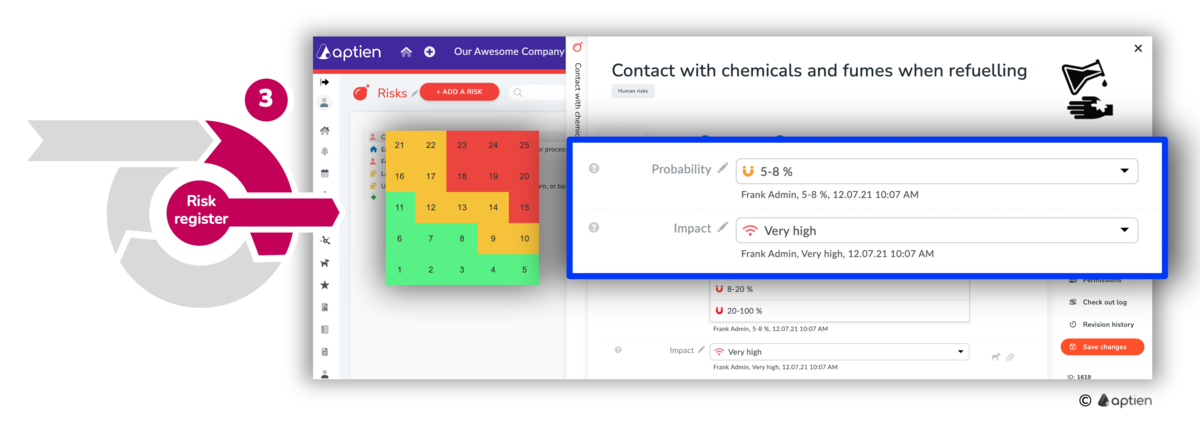
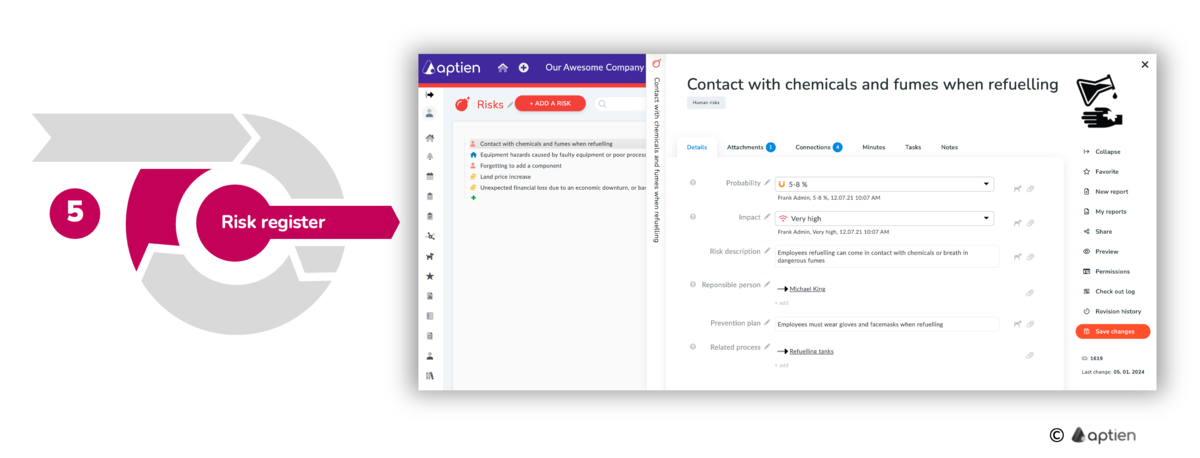
How to create a risk catalog
You can create a risk catalog using the risk register. You create a separate risk card for each risk, where you keep detailed information such as impact, probability and also measures to eliminate or mitigate the impact. You keep the risks in context, so you know what risk is associated with what asset - project, asset, process and other assets, as well as who is responsible for what risk.
How to create a risk map
For risks, you set up your risk map, where you can prioritize and monitor risks according to the defined zones in the risk map. Click on the desired zone and the risks are filtered according to the criteria you set.
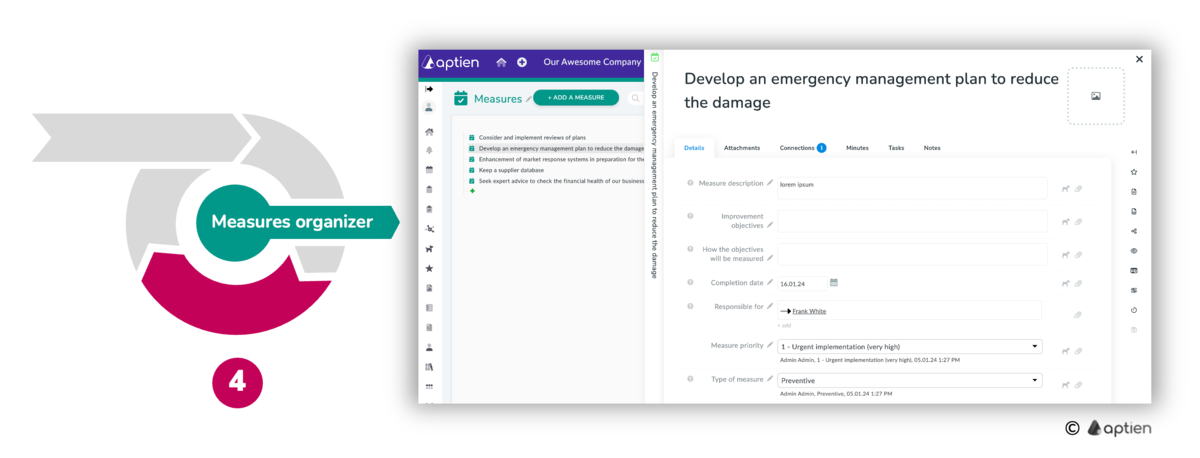
How to create and manage measures
For selected risks, you create corrective actions in a separate corrective or preventive action organizer. For each measure, you create a separate record on which you keep detailed information and use assigned tasks to manage and control work on them. You keep risks and their measures in context, i.e. you know which risk is associated with which measure and who is responsible for which measure.
How to reassess risks
The situation is constantly changing over time. New risks arise and the original ones may disappear or their impact or probability of occurrence may change. This must be taken into account and at least once a year the risks must be reassessed and the subsequent measures taken with them.
Continuous monitoring and evaluation of the state of risks is therefore important. Evaluating measures, reporting significant risks and measures to eliminate or mitigate risks. This can be done in different ways. Formal evaluation takes place in the form of audits, from which suggestions for improvement or re-evaluation follow.
How to report incidents in your company
Incidents are potentially an indicator of events that lead to risks. If you need to establish a systematic control and reporting of incidents in your company, use incident reporting.